Cotrimoxazole Induced Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis: A Clinical Case
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.60591/crspmi.330Keywords:
Stevens-Johnson Syndrome/etiology, Trimethoprim, Sulfamethoxazole Drug Combination/adverse effectsAbstract
We present the case of a 53-year-old man, with no relevant personal medical history who was on the seventeenth day of treatment with cotrimoxazole after a diagnosis of a urinary tract infection.
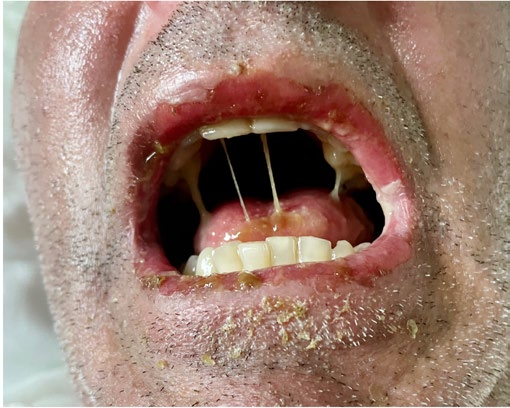
He was admitted to the emergency department complaining of a pruritic maculopapular rash that was widespread, with particular emphasis on the torso and sparing the palms of the hands and soles of the feet, bilateral conjunctival hyperemia, lip edema, and odynophagia.
After an extensive study was conducted, the conclusion was that it was a side effect of the ongoing treatment, and the antibiotic was promptly suspended. However, the skin and mucosal lesions progressed unfavorably, with an increase in the affected area and an important involvement of the oral and ocular mucosa with extensive erosions. The diagnosis of toxic epidermal necrosis was made, a rare entity that occurs as a side effect of commonly prescribed antibiotics and other drugs.
Downloads
References
Oliveira A, Sanches M, Selores M. O espectro clínico síndrome de Stevens-Johnson e necrólise epidérmica tóxica. Acta Med Port. 2011;24:995-1002.
Lee EY, Knox C, Phillips EJ. Worldwide Prevalence of Antibiotic-Associated Stevens-Johnson Syndrome and Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. JAMA Dermatol. 2023;159:384-92. doi:
1001/jamadermatol.2022.6378.
Charlton OA, Harris V, Phan K, Mewton E, Jackson C, Cooper A. Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis and Steven-Johnson Syndrome: A Comprehensive Review. Adv Wound Care (New Rochelle). 2020;9:426-39. doi: 10.1089/wound.2019.0977.
Frantz R, Huang S, Are A, Motaparthi K. Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis: a review of diagnosis and management. Medicina (Kaunas). 2021;57:895. doi: 10.3390/medicina57090895.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Carolina Veiga

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.






