Úlcera Escrotal Devido ao Uso de Lenvatinib Durante o Tratamento de Carcinoma Hepatocelular Irressecável
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.60591/crspmi.328Keywords:
Carcinoma Hepatocellular/tratamento farmacológico, Lenvatinib/efeitos adversos, Úlcera da Pele/ induzida quimicamenteAbstract
O lenvatinib é um fármaco usado em doentes com carcinoma hepatocelular (CHC) irressecável, devido à sua atividade antiangiogénica. Esta classe de fármacos mudou o paradigma do tratamento do CHC mas apresenta agora um desafio adicional devido aos efeitos secundários significativamente
diferentes comparativamente à quimioterapia convencional.
Apresentamos o caso de um homem de 58 anos com cirrose alcoólica e dismetabólica em estádio Child-Pugh A, diagnosticado com CHC irresecável, estadio C segundo o sistema BCLC (Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer).
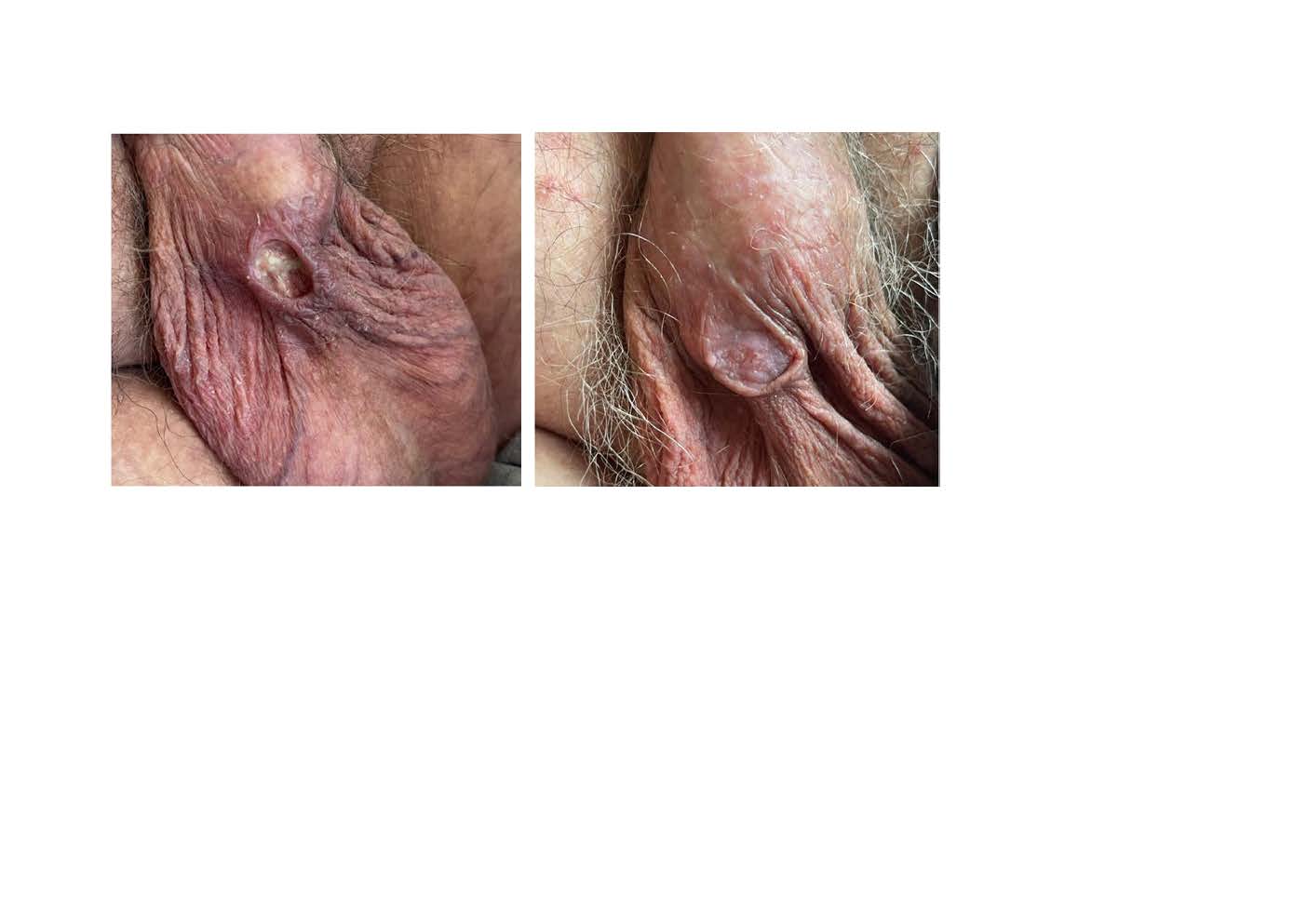
O doente iniciou tratamento com lenvatinib e, após 4 meses, desenvolveu uma úlcera cutânea no escroto, o que levou a uma investigação adicional sobre a sua causa e posteriormente à suspensão do lenvatinib. Com a interrupção do fármaco (sem tratamento específico), a úlcera resolveu.
Este caso reforça a importância de vigiar efeitos adversos cutâneos associados ao lenvatinib que resultam provavelmente da sua atividade antiangiogénica.
Downloads
References
Kudo M, Finn RS, Qin S, Han KH, Ikeda K, Piscaglia F, et al. Lenvatinib versus sorafenib in first-line treatment of patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: a randomised phase 3 non-inferiority trial. Lancet. 2018;391:1163-73. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(18)30207-1.
Reig M, Forner A, Rimola J, Ferrer-Fàbrega J, Burrel M, Garcia-Criado Á, et al. BCLC strategy for prognosis prediction and treatment recommendation: The 2022 update. J Hepatol. 2022;76:681–93. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2021.11.018
Goel A, Singla A. Lenvatinib: A narrative drug review. Cancer Res Stat Treat. 2021;4:709.
Matsuki M, Hoshi T, Yamamoto Y, Ikemori-Kawada M, Minoshima Y, Funahashi Y, et al. Lenvatinib inhibits angiogenesis and tumor fibroblast growth factor signaling pathways in human hepatocellular carcinoma models. Cancer Med. 2018;7:2641-53. doi: 10.1002/cam4.1517.
Rimassa L, Danesi R, Pressiani T, Merle P. Management of adverse events associated with tyrosine kinase inhibitors: Improving outcomes for patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Treat Rev. 2019;77:20-8. doi: 10.1016/j.ctrv.2019.05.004.
Barone M, Grani G, Ramundo V, Garritano T, Durante C, Falcone R. Fournier's gangrene during lenvatinib treatment: A case report. Mol Clin Oncol. 2020;12:588-91. doi: 10.3892/mco.2020.2031.
Kim BH, Yu SJ, Kang W, Cho SB, Park SY, Kim SU, et al. Expert consensus on the management of adverse events in patients receiving lenvatinib for hepatocellular carcinoma. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022;37:428-39. doi: 10.1111/jgh.15727.
Ikeda M, Kobayashi M, Tahara M, Kaneko S. Optimal management of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma treated with lenvatinib. Expert Opin Drug Saf. 2018;17:1095–105. doi: 10.1080/14740338.2018.1530212
Cha S, Kim DW, Choe JW, Kim TH, Kim SY, Hyun JJ, et al. A case report of a patient presented with skin ulcer after treatment of lenvatinib. J Liver Cancer. 2021;21:194–8. doi: 10.17998/jlc.2021.09.20.
Naranjo CA, Busto U, Sellers EM, Sandor P, Ruiz I, Roberts EA, et al. A method for estimating the probability of adverse drug reactions. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1981;30:239-45. doi: 10.1038/clpt.1981.154.
Dohmen K. Severe ulcerative skin lesions due to lenvatinib. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020;18:e113. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2019.05.005
Kitamura M, Hayashi T, Suzuki C, Hirano S, Tateya I, Kishimoto Y, et al. Successful recovery from a subclavicular ulcer caused by lenvatinib for thyroid cancer: a case report. World J Surg Oncol. 2017;15:24. doi: 10.1186/s12957-017-1096-5.
Sally R, Ugonabo N, Nguyen A, Kim RH, Lo Sicco K. Lenvatinib-induced psoriasiform eruption and palmoplantar erythema in a patient with hepatocellular carcinoma. JAAD Case Rep. 2021;15:1-3. doi: 10.1016/j.jdcr.2021.07.001.
Zuo RC, Apolo AB, DiGiovanna JJ, Parnes HL, Keen CM, Nanda S, Dahut WL CE. Cutaneous adverse effects associated with the tyrosine-kinase inhibitor cabozantinib. JAMA Dermatol. 2015;151:170–7. doi: 10.1001/jamadermatol.2014.2734
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
Categories
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Cecília Moreira

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.






