Exuberant Intra-Abdominal Abscesses Secondary to Streptococcus Anginosus: A Diagnostic and Therapeutic Challenge
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.60591/crspmi.390Keywords:
Abdominal Abscess/diagnosis, Abdominal Abscess/therapy, Intraabdominal Infections/diagnostic imaging, Streptococcal Infections, Streptococcus anginosusAbstract
The group Streptococcus anginosus is comprised of bacteria that are usually indolent and commensal in nature, with a limited role as infective agents in healthy patients. They can, however, act as opportunistic agents in patients with serious comorbidities, and are usually associated with abscesses.
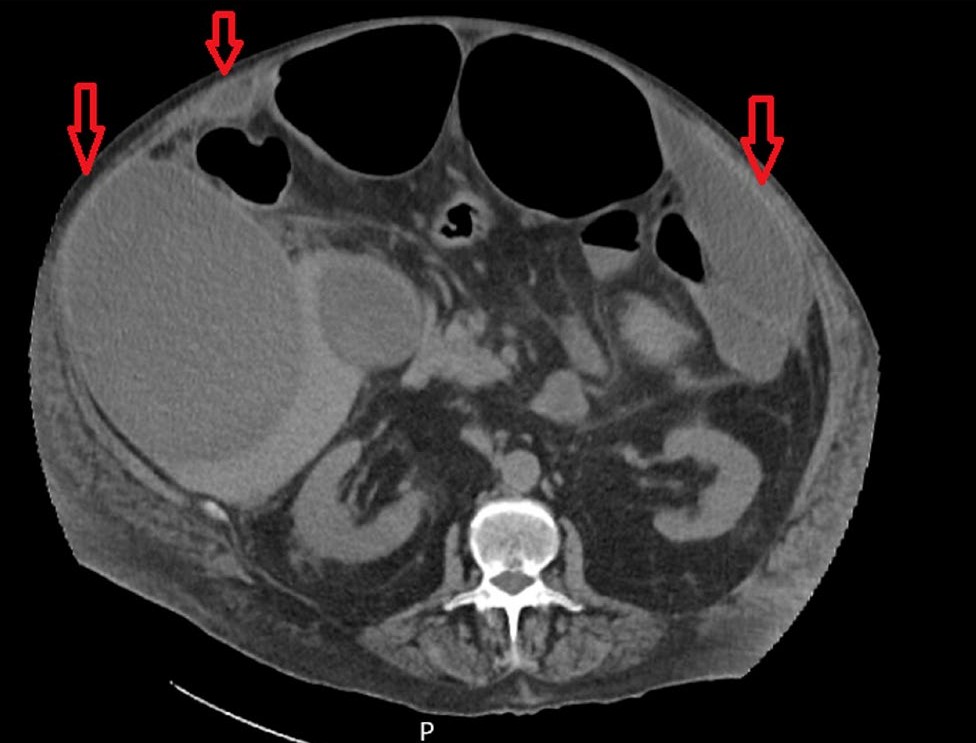
We present the case of a 63-year-old male patient with multiple comorbidities, including diabetes mellitus, admitted due to acute heart failure. He presented with fever, coughing, polypnea and abdominal distension. Due to slight but persistent liver enzyme elevation an ultrasound was requested, revealing massive liver and abdominal wall abscesses. Pus culture was positive for Streptococcus anginosus. Although initial response was favourable, with abscess reduction after percutaneous drainage, there was a need for further drainage and multiple broad-spectrum antibiotic regimens.
We highlight this case due to the exuberant abscesses, the difficulty in treating them, as well as the uncommon aetiology caused by Streptococcus anginosus.
Downloads
References
1. Jiang S, Li M, Fu T, Shan F, Jian L, Shao Z. Clinical Characteristics of Infections Caused by Streptococcus Anginosus Group. Sci Rep. 2020; 10: 9032 doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-65977-z.
2. Pilarczyk-Zurek M, Sitkiewicz I, Koziel J. The Clinical View on Streptococcus anginosus Group - Opportunistic Pathogens Coming Out of Hiding. Front Microbiol. 2022; 8:13:956677 doi:10.3389/fmicb.2022.956677.
3. Kaplan NM, Khader YS, Ghabashineh DM. Laboratory Diagnosis, Antimicrobial Susceptibility And Genuine Clinical Spectrum of Streptococcus anginosus Group; Our Experience At A University Hospital. Med Arch.2022; 252-8. doi:10.5455/medarh.2022.76.252-258.
4. Murarka S, Pranav F, Dandavate V. Pyogenic liver abscess secondary to disseminated streptococcus anginosus from sigmoid diverticulitis. J Glob Infect Dis. 2011;3:79–81. doi:10.4103/0974-777X.77300
5. Ismail K, Hughes I, Moloney S, Grimwood K. Streptococcus anginosus group infections in hospitalised children and young people. J Paediatr Child Health. 2022;58:809-14. doi: 10.1111/jpc.15840
6. Al Majid F, Aldrees A, Barry M, Binkhamis K, Allam A, Almohaya A. Streptococcus anginosus group infections: Management and outcome at a tertiary care hospital. J Infect Public Health. 2020; 13:1749-54. doi: 10.1016/j.jiph.2020.07.017.
7. Tasaduq Fazili T, Riddell S, Kiksa D, Giurgea L, Sharngoe C, Javaid W. Streptococcus anginosus Group Bacterial infections. Am J Med Sci. 2017;354:257-61. doi: 10.1016/j.amjms.2017.05.011
8. Jousimies-Somer H, Savolainen S, Mäkitie A, Ylikoski J. Bacteriologic findings in peritonsillar abscesses in young adults. Clin Infect Dis. 1993; 16:S292-8. doi: 10.1093/clinids/16.supplement_4.s292
9. Madathil S, Matsumoto S, Mathews KD, Glykys J. Central Nervous System Infections Due to Streptococcus anginosus Group: A Single-Center Case Series. J Child Neurol. 2022; 37:210-7. doi: 10.1177/08830738211052132
10. Berbudi A, Rahmadika N, Tjahjadi AI, Ruslami R. Type 2 Diabetes and its Impact on the Immune System. Curr Diabetes Rev. 2020; 16:442–9. doi: 10.2174/1573399815666191024085838
11. Wang YH. Current progress of research on intestinal bacterial translocation. Microb Pathog. 2020:104652. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2020.104652
12. Jin S, Wetzel D, Schirmer M. Deciphering mechanisms and implications of bacterial translocation in human health and disease. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2022;67:102147. doi: 10.1016/j.mib.2022.102147
13. Cancela Costa A, Grass F, Andres Cano I, Desgranges F, Delabays C, Kritikos A, et al. Antibacterial and antifungal drug concentrations in intra-abdominal abscesses: a prospective clinical study. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2025;69:e0117824. doi: 10.1128/aac.01178-24
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
Categories
License
Copyright (c) 2025 José Santos, Jorge Leitão, Arsénio Santos, Lèlita Santos

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.






